LinuxStat

For reading the eyecandy HTML version, visit linux_stat.
LinuxStat lets you read status of a Linux system. It can show you cpu stats and usages, memory stats and usages, swap stats and usages, battery usage, bios info, kernel details, local ip, os details and parse os-release + lsb-release, etc.
It only works for Linux, and detecting the OS is upto the user of this gem.
Dependencies:
- You need to have the C compiler installed to be able to compile the C extensions.
On Arch Linux:
# pacman -S gcc make
On Debian based systems:
# apt install gcc build-essential
You might also require ruby-dev in Debian based systems which provides support for ruby.h header file:
# apt install ruby-devOnce your are done, and you can compile the C file, you can follow the installation!
Installation
Add this line to your application's Gemfile:
gem 'linux_stat'
And then execute:
$ bundle install
Or install it yourself as:
$ gem install linux_stat
Usage
LinuxStat::BIOS
LinuxStat::BIOS.date
=> "04/10/2017"
LinuxStat::BIOS.model
=> "Inspiron 5567"
LinuxStat::BIOS.vendor
=> "Dell Inc."
LinuxStat::BIOS.version
=> "1.1.2"
LinuxStat::Battery
LinuxStat::Battery.charge
=> 100.0
LinuxStat::Battery.charging?
=> true
LinuxStat::Battery.discharging?
=> false
LinuxStat::Battery.full?
=> true
LinuxStat::Battery.manufacturer
=> "Samsung SDI"
LinuxStat::Battery.model
=> "DELL CYMGM77"
LinuxStat::Battery.present?
=> true
LinuxStat::Battery.stat
=> {:model=>"DELL CYMGM77", :manufacturer=>"Samsung SDI", :technology=>"Li-ion", :status=>"Full", :charge=>100.0, :charging=>true, :discharging=>false, :full=>true}
LinuxStat::Battery.status
=> "Full"
LinuxStat::Battery.technology
=> "Li-ion"
LinuxStat::CPU
LinuxStat::CPU.count
=> 4
LinuxStat::CPU.cur_freq
=> [2000063, 2000108, 2000332, 2000028]
LinuxStat::CPU.max_freq
=> [2000000, 2000000, 2000000, 2000000]
LinuxStat::CPU.model
=> "Intel(R) Core(TM) i3-6006U CPU @ 2.00GHz"
LinuxStat::CPU.stat
=> {0=>0.0, 1=>0.0, 2=>0.0, 3=>0.0, 4=>0.0}
LinuxStat::CPU.total_usage
=> 0.0
LinuxStat::CPU.usage
=> 20.0
LinuxStat::CPU.usages
=> {0=>20.0, 1=>0.0, 2=>0.0, 3=>50.0, 4=>100.0}
LinuxStat::Filesystem
LinuxStat::Filesystem.available
=> 33120964608
LinuxStat::Filesystem.free
=> 33120964608
LinuxStat::Filesystem.stat
=> {:total=>119981191168, :free=>33120964608, :used=>86860226560}
LinuxStat::Filesystem.stat_raw
=> {:block_size=>4096, :fragment_size=>4096, :blocks=>29292283, :block_free=>8086173, :block_avail_unpriv=>8086173, :inodes=>58612160, :free_inodes=>56567338, :filesystem_id=>2050, :mount_flags=>1024, :max_filename_length=>255}
LinuxStat::Filesystem.total
=> 119981191168
LinuxStat::Filesystem.used
=> 86860226560
LinuxStat::Kernel
LinuxStat::Kernel.build_date
=> 2020-11-20 07:44:55 +0000
LinuxStat::Kernel.build_date_string
=> "20 Nov 2020 07:44:55 +0000"
LinuxStat::Kernel.build_user
=> "souravgoswami@archlinux"
LinuxStat::Kernel.clk_tck
=> 100
LinuxStat::Kernel.compiler
=> [:gcc, "10.2.0"]
LinuxStat::Kernel.compiler_version
=> "10.2.0"
LinuxStat::Kernel.release
=> "5.9.9-xanmod1-1"
LinuxStat::Kernel.string
=> "Linux version 5.9.9-xanmod1-1 (souravgoswami@archlinux) (gcc (GCC) 10.2.0, GNU ld (GNU Binutils) 2.35.1) #1 SMP PREEMPT Fri, 20 Nov 2020 07:44:55 +0000"
LinuxStat::Kernel.ticks
=> 100
LinuxStat::Kernel.version
=> "5.9.9-xanmod1-1"
LinuxStat::Memory
LinuxStat::Memory.available
=> 579264
LinuxStat::Memory.percent_available
=> 15.1
LinuxStat::Memory.percent_used
=> 84.9
LinuxStat::Memory.stat
=> {:total=>3836236, :used=>3256972, :available=>579264, :percent_used=>84.9, :percent_available=>15.1}
LinuxStat::Memory.total
=> 3836236
LinuxStat::Memory.used
=> 3256972
LinuxStat::Mounts
LinuxStat::Mounts.device_stat
=> {:mountpoint=>"/", :total=>119981191168, :free=>33120964608, :available=>33120964608, :used=>86860226560, :percent_used=>72.39, :percent_free=>27.61, :percent_available=>27.61}
LinuxStat::Mounts.devices_stat
=> {"proc"=>{:mountpoint=>"/proc", :total=>0, :free=>0, :available=>0, :used=>0, :percent_used=>NaN, :percent_free=>NaN, :percent_available=>NaN}, "sys"=>{:mountpoint=>"/sys", :total=>0, :free=>0, :available=>0, :used=>0, :percent_used=>NaN, :percent_fre...
LinuxStat::Mounts.list
=> ["proc /proc proc rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime 0 0", "sys /sys sysfs rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime 0 0", "dev /dev devtmpfs rw,nosuid,relatime,size=1892908k,nr_inodes=473227,mode=755 0 0", "run /run tmpfs rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,mode=755 0 0", "...
LinuxStat::Mounts.list_devices
=> ["proc", "sys", "dev", "run", "/dev/sda2", "securityfs", "tmpfs", "devpts", "tmpfs", "cgroup2", "cgroup", "pstore", "none", "cgroup", "cgroup", "cgroup", "cgroup", "cgroup", "cgroup", "cgroup", "cgroup", "cgroup", "cgroup", "cgroup", "systemd-1", "deb...
LinuxStat::Mounts.list_devices_mount_point
=> {"proc"=>"/proc", "sys"=>"/sys", "dev"=>"/dev", "run"=>"/run", "/dev/sda2"=>"/", "securityfs"=>"/sys/kernel/security", "tmpfs"=>"/run/user/1000", "devpts"=>"/dev/pts", "cgroup2"=>"/sys/fs/cgroup/unified", "cgroup"=>"/sys/fs/cgroup/perf_event", "pstore...
LinuxStat::Mounts.mount_point
=> "/"
LinuxStat::Mounts.root
=> "/dev/sda2"
LinuxStat::Mounts.root_fs
=> "xfs"
LinuxStat::Mounts.root_mount_options
=> "rw,noatime,attr2,inode64,logbufs=8,logbsize=32k,noquota"
LinuxStat::Mounts.tmpfs
=> {"/dev/shm"=>"tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs rw,nosuid,nodev 0 0", "/sys/fs/cgroup"=>"tmpfs /sys/fs/cgroup tmpfs ro,nosuid,nodev,noexec,size=4096k,nr_inodes=1024,mode=755 0 0", "/cache"=>"tmpfs /cache tmpfs rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,size=2097152k 0 0", "/ramdisk...
LinuxStat::Net
LinuxStat::Net.current_usage
=> {:received=>2183400.0, :transmitted=>114860.0}
LinuxStat::Net.ipv4_private
=> "192.168.0.102"
LinuxStat::Net.total_bytes
=> {:received=>294316415, :transmitted=>45313147}
LinuxStat::Net.total_bytes_received
=> 294317913
LinuxStat::Net.total_bytes_transmitted
=> 45313147
LinuxStat::Net.usage
=> {:received=>1643690.0, :transmitted=>146030.0}
LinuxStat::OS
LinuxStat::OS.bits
=> 64
LinuxStat::OS.distribution
=> "Arch Linux"
LinuxStat::OS.hostname
=> "archlinux"
LinuxStat::OS.lsb_release
=> {:LSB_VERSION=>"1.4", :DISTRIB_ID=>"Arch", :DISTRIB_RELEASE=>"rolling", :DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION=>"Arch Linux"}
LinuxStat::OS.machine
=> "x86_64"
LinuxStat::OS.nodename
=> "archlinux"
LinuxStat::OS.os_release
=> {:NAME=>"Arch Linux", :PRETTY_NAME=>"Arch Linux", :ID=>"arch", :BUILD_ID=>"rolling", :ANSI_COLOR=>"38;2;23;147;209", :HOME_URL=>"https://www.archlinux.org/", :DOCUMENTATION_URL=>"https://wiki.archlinux.org/", :SUPPORT_URL=>"https://bbs.archlinux.org/"...
LinuxStat::OS.uptime
=> {:hour=>7, :minute=>44, :second=>29.92}
LinuxStat::Process
LinuxStat::Process.count
=> 205
LinuxStat::Process.idle
=> [3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 23, 30, 37, 39, 49, 102, 103, 104, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 117, 118, 120, 122, 131, 134, 140, 152, 153, 166, 168, 172, 174, 176, 178, 182, 183, 184, 185, 186, 188, 230, 271, 324, 328, 337, 14228, 14757, 14998, 14999, 15000, 15001, 15...
LinuxStat::Process.list
=> [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 102, 103, 104, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 114, 115, 117, 118, 120, 122, 131, 134,...
LinuxStat::Process.names
=> {1=>"systemd", 2=>"kthreadd", 3=>"rcu_gp", 4=>"rcu_par_gp", 6=>"kworker/0:0H", 9=>"mm_percpu_wq", 10=>"ksoftirqd/0", 11=>"rcuc/0", 12=>"rcu_preempt", 13=>"rcub/0", 14=>"migration/0", 15=>"idle_inject/0", 16=>"cpuhp/0", 17=>"cpuhp/1", 18=>"idle_inject/...
LinuxStat::Process.running
=> [21158]
LinuxStat::Process.sleeping
=> [1, 2, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 38, 40, 41, 42, 46, 47, 48, 50, 51, 52, 111, 114, 115, 165, 167, 189, 217, 231, 302, 307, 308, 309, 310, 320, 321, 322, 323, 325, 326, 350, 353, 356, 374, 394,...
LinuxStat::Process.types
=> {1=>:sleeping, 2=>:sleeping, 3=>:idle, 4=>:idle, 6=>:idle, 9=>:idle, 10=>:sleeping, 11=>:sleeping, 12=>:idle, 13=>:sleeping, 14=>:sleeping, 15=>:sleeping, 16=>:sleeping, 17=>:sleeping, 18=>:sleeping, 19=>:sleeping, 20=>:sleeping, 21=>:sleeping, 23=>:i...
LinuxStat::Process.zombie
=> []
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.cmdline
=> "ruby exe/linuxstat.rb -md"
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.command_name
=> "ruby"
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.cpu_stat
=> {:cpu_usage=>0.0, :threads=>1, :last_executed_cpu=>1}
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.cpu_usage
=> 0.0
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.gid
=> {:real=>1000, :effective=>1000, :saved_set=>1000, :filesystem_uid=>1000}
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.last_executed_cpu
=> 1
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.mem_stat
=> {:memory=>10051.584, :virtual_memory=>81801.216, :resident_memory=>15986.688}
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.memory
=> 10051.584
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.owner
=> "sourav"
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.resident_memory
=> 15986.688
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.threads
=> 1
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.total_io
=> {:read_bytes=>0, :write_bytes=>0}
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.uid
=> {:real=>1000, :effective=>1000, :saved_set=>1000, :filesystem_uid=>1000}
LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.virtual_memory
=> 81801.216
LinuxStat::Swap
LinuxStat::Swap.any?
=> true
LinuxStat::Swap.available
=> 3383720
LinuxStat::Swap.list
=> {"/dev/zram0"=>[:partition, 4194300, 810580, -2]}
LinuxStat::Swap.percent_available
=> 80.67
LinuxStat::Swap.percent_used
=> 19.33
LinuxStat::Swap.stat
=> {:total=>4194300, :used=>810580, :available=>3383720, :percent_used=>19.33, :percent_available=>80.67}
LinuxStat::Swap.total
=> 4194300
LinuxStat::Swap.used
=> 810580
LinuxStat::Sysconf
LinuxStat::Sysconf.child_max
=> 2000000
LinuxStat::Sysconf.get_euid
=> 1000
LinuxStat::Sysconf.get_gid
=> 1000
LinuxStat::Sysconf.get_login
=> "sourav"
LinuxStat::Sysconf.get_uid
=> 1000
LinuxStat::Sysconf.get_user
=> "sourav"
LinuxStat::Sysconf.hostname_max
=> 64
LinuxStat::Sysconf.login_name_max
=> 256
LinuxStat::Sysconf.open_max
=> 1024
LinuxStat::Sysconf.pagesize
=> 4096
LinuxStat::Sysconf.posix_version
=> 200809
LinuxStat::Sysconf.sc_clk_tck
=> 100
LinuxStat::Sysconf.stream_max
=> 16
LinuxStat::Sysconf.tty_name_max
=> 32
LinuxStat::Uname
LinuxStat::Uname.machine
=> "x86_64"
LinuxStat::Uname.nodename
=> "archlinux"
LinuxStat::Uname.release
=> "5.9.9-xanmod1-1"
LinuxStat::Uname.sysname
=> "Linux"
LinuxStat::Uname.version
=> "#1 SMP PREEMPT Fri, 20 Nov 2020 07:44:55 +0000"
LinuxStat::User
LinuxStat::User.get_current_user
=> "sourav"
LinuxStat::User.get_euid
=> 1000
LinuxStat::User.get_gid
=> 1000
LinuxStat::User.get_login
=> "sourav"
LinuxStat::User.get_uid
=> 1000
LinuxStat::User.get_user
=> "sourav"
LinuxStat::User.gid_by_username
=> 1000
LinuxStat::User.gids
=> {:root=>0, :bin=>1, :daemon=>2, :mail=>12, :ftp=>11, :http=>33, :nobody=>65534, :dbus=>81, :"systemd-journal-remote"=>982, :"systemd-network"=>981, :"systemd-resolve"=>980, :"systemd-timesync"=>979, :"systemd-coredump"=>978, :uuidd=>68, :avahi=>977, :...
LinuxStat::User.home_by_gid
=> "/home/sourav"
LinuxStat::User.home_by_username
=> "/home/sourav"
LinuxStat::User.home_directories
=> {:root=>"/root", :bin=>"/", :daemon=>"/", :mail=>"/var/spool/mail", :ftp=>"/srv/ftp", :http=>"/srv/http", :nobody=>"/", :dbus=>"/", :"systemd-journal-remote"=>"/", :"systemd-network"=>"/", :"systemd-resolve"=>"/", :"systemd-timesync"=>"/", :"systemd-c...
LinuxStat::User.homes_by_uid
=> ["/home/sourav"]
LinuxStat::User.ids
=> {:root=>{:uid=>0, :gid=>0}, :bin=>{:uid=>1, :gid=>1}, :daemon=>{:uid=>2, :gid=>2}, :mail=>{:uid=>8, :gid=>12}, :ftp=>{:uid=>14, :gid=>11}, :http=>{:uid=>33, :gid=>33}, :nobody=>{:uid=>65534, :gid=>65534}, :dbus=>{:uid=>81, :gid=>81}, :"systemd-journal...
LinuxStat::User.list
=> ["root", "bin", "daemon", "mail", "ftp", "http", "nobody", "dbus", "systemd-journal-remote", "systemd-network", "systemd-resolve", "systemd-timesync", "systemd-coredump", "uuidd", "avahi", "colord", "git", "lxdm", "polkitd", "rtkit", "usbmux", "sourav...
LinuxStat::User.uid_by_username
=> 1000
LinuxStat::User.uids
=> {:root=>0, :bin=>1, :daemon=>2, :mail=>8, :ftp=>14, :http=>33, :nobody=>65534, :dbus=>81, :"systemd-journal-remote"=>982, :"systemd-network"=>981, :"systemd-resolve"=>980, :"systemd-timesync"=>979, :"systemd-coredump"=>978, :uuidd=>68, :avahi=>977, :c...
LinuxStat::User.username_by_gid
=> "sourav"
LinuxStat::User.usernames_by_uid
=> ["sourav"]
Note 1: CPU usage, and Net usage
To calculate the current usage, we need to get two usages at a given interval, and subtract the 2nd from the 1st.
For example, if the current download (LinuxStat::Net.total_bytes_received) is 1000 bytes, and if 0.1 seconds ago, it was 100 bytes, that means 900 bytes was received in 0.1 seconds.
That means the current speed is 9000 bytes/s or 9 kB/s.
Without the polling, it's not really possible to calculate the current usage. Although the total usage can be calculated. A system monitor does that, too...
Thus these methods requires a polling interval:
- LinuxStat::CPU.stat, usage, total_usage, usage.
- LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.cpu_usage, cpu_stat.
- LinuxStat::Net.usage, current_usage.
They sleep for a given interval and then differentiate between the data.
For more info look at the ri documentation for the above methods.
These methods can slow down your application a bit unless you implement them in a thread.
Other methods doesn't have the sleep implemented, and they just works under a millisecond.
For example:
LinuxStat::CPU.stat(0.1)
=> {0=>7.69, 1=>0.0, 2=>0.0, 3=>18.18, 4=>10.0}
This will sleep for 0.1 seconds. To be reliable, use a time like 0.05 seconds or so.
If you want to build a system monitor and don't want to wait, you have to do something like this:
#!/usr/bin/ruby
require 'linux_stat'
usages = []
thread = Thread.new { }
counter = 0
while true
thread = Thread.new { usages = LinuxStat::CPU.usages(0.5).values } unless thread.alive?
# clears the screen and prints the info
puts "\e[2J\e[H\e[3J"\
"#{counter += 1}\n"\
"\e[1;33mTotal CPU Usage:\e[0m #{usages[0]}%\n"\
"#{usages[1..-1].to_a.map.with_index { |x, i| "\e[1;33mCore #{i}\e[0m => #{x}%\n" }.join}"\
"Total Download: #{LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_decimal LinuxStat::Net.total_bytes_received}\n"\
"Total Upload: #{LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_decimal LinuxStat::Net.total_bytes_transmitted}"
end
This will not wait in every loop for 0.5 seconds, but it will not update the cpu usage in every loop either. So what you will be seeing in the CPU usage in every 0.5 seconds interval.
You will also see the counter increases like crazy. Which means it's not getting waited for 0.5 seconds.
But the other methods doesn't have this delay, thus in this example, you will be able see the "Total Download" and "Total Upload" in real time, well as soon as the Linux kernel updates the data and ruby executes the loop.
Just run the linuxstat.rb command to test what method takes what time measured in microseconds.
Note 2: Filesystem
Filesystem can take arguments. By default it's '/' or the root of the system...
But for the sake of example, to get the free disk space of /, you do:
$ irb
irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat'
=> true
irb(main):002:0> LinuxStat::Filesystem.free('/').fdiv(1024 ** 3).to_s << " GiB"
=> "35.666873931884766 GiB"
To see the free and total space of a thumbdrive:
$ irb
irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat'
=> true
irb(main):002:0> LinuxStat::Mounts.mount_point('/dev/sdb1')
=> "/run/media/sourav/5c2b7af7-d4c3-4ab4-a035-06d18ffc8e6f"
irb(main):003:0> thumbdrive = _
=> "/run/media/sourav/5c2b7af7-d4c3-4ab4-a035-06d18ffc8e6f"
irb(main):004:0> LinuxStat::Filesystem.free(thumbdrive).fdiv(1024 ** 3).to_s << " GiB"
=> "2.504791259765625 GiB"
irb(main):005:0> LinuxStat::Filesystem.total(thumbdrive).fdiv(1024 ** 3).to_s << " GiB"
=> "29.305004119873047 GiB"
Note 3: ProcessInfo
All the methods LinuxStat::ProcessInfo can take an argument containing the Process ID of a process. By default it's $$ or the PID of the current process, ruby, itself.
Example: Say you want to see how much CPU Firefox is consuming, for that you have to do the following (firefox can create a lot of child process though):
Get the PID of Firefox:
LinuxStat::Process.names.find { |x| x[1].include? 'firefox' }[0] => 770 # but this differs all the timeGet the CPU usage:
$ irb irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat' => true
irb(main):002:0> pid = LinuxStat::Process.names.find { |x| x[1].include? 'firefox' }[0] => 770
irb(main):003:0> LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.cpu_usage(pid: pid) => 0.0
irb(main):004:0> LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.cpu_usage(pid: pid) => 15.0
To get the memory usage of Firefox (for example):
$ irb irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat' => true
irb(main):002:0> LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.mem_stat(LinuxStat::Process.names.find { |x| x[1].include? 'firefox'.freeze }[0]) => :virtual_memory=>4754080, :resident_memory=>814388
To get ONLY the memory usage in MiB:
$ irb irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat' => true
irb(main):002:0> LinuxStat::ProcessInfo.memory(LinuxStat::Process.names.find { |x| x[1].include? 'firefox'.freeze }[0]).fdiv(1024).round(2).to_s << " MiB" => "467.51 MiB"
## Note 4: FS
LinuxStat::FS module gives you the raw info in Hash collected from statvfs.
It's not documented above because it's not suggested to run this directly. But it shouldn't cause any issue. `LinuxStat::Filesystem.stat_raw(fs = '/')` does that automatically.
It always requires an argument, and it's very fast. It directly calls the C API without any intermediate Ruby code.
For example, to get the info about '/' or root:
$ irb irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat' => true
irb(main):002:0> LinuxStat::FS.stat('/') => :fragment_size=>4096, :blocks=>29292283, :block_free=>9349843, :block_avail_unpriv=>9349843, :inodes=>58612160, :free_inodes=>56708247, :filesystem_id=>2050, :mount_flags=>1024, :max_filename_length=>255
irb(main):003:0> t = Time.now ; puts LinuxStat::FS.stat('/') ; Time.now - t :fragment_size=>4096, :blocks=>29292283, :block_free=>9349843, :block_avail_unpriv=>9349843, :inodes=>58612160, :free_inodes=>56708247, :filesystem_id=>2050, :mount_flags=>1024, :max_filename_length=>255 => 5.0468e-05
To learn more about them, just run ri and the method name. To see all available methods.
## Note 5: User
Most of the LinuxStat::User supports arguments.
For example, to get a user's home by the username:
$ irb irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat' => true
irb(main):002:0> LinuxStat::User.home_by_username('root') => "/root"
irb(main):003:0> LinuxStat::User.home_by_username('ftp') => "/srv/ftp"
irb(main):004:0> LinuxStat::User.home_by_username('mail') => "/var/spool/mail"
Or to get the user's home by the GID/UID:
$ irb irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat' => true
irb(main):002:0> LinuxStat::User.homes_by_uid(1001) => ["/home/userx", "/home/userz"]
irb(main):003:0> LinuxStat::User.homes_by_uid(1000) => ["/home/sourav"]
irb(main):004:0> LinuxStat::User.home_by_gid(1001) => "/home/userx"
irb(main):005:0> LinuxStat::User.home_by_gid(1000) => "/home/sourav"
irb(main):006:0> LinuxStat::User.home_by_gid(0) => "/root"
Or to get the UID/GID by username:
$ irb irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat' => true
irb(main):002:0> LinuxStat::User.uid_by_username('root') => 0
irb(main):003:0> LinuxStat::User.uid_by_username('ftp') => 14
irb(main):004:0> LinuxStat::User.gid_by_username('ftp') => 11
irb(main):005:0> LinuxStat::User.gid_by_username('InvalidUser') => nil
Or to get the current user (in docker for example):
$ irb irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat' => true
irb(main):002:0> LinuxStat::User.get_current_user => "x"
irb(main):003:0> LinuxStat::User.get_user => "x"
irb(main):004:0> LinuxStat::User.get_login => ""
Right, the get_login() can return an empty string. But LinuxStat::User.get_user also aliased as LinuxStat::User.get_current_user shouldn't return an empty string under most circumstances.
## Note 6: PrettifyBytes
Often times we need to work with KB, MB GB, TB, or KiB, MiB, GiB, TiB, etc.
And we need some work to convert bytes to those units.
Because LinuxStat provides a lot of data in bytes, and kilobytes, it's quite tedious to convert them all the time.
To avoid such duplication, it comes with a PrettifyBytes module.
For example, to convert bytes to decimal suffixes:
$irb irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat' => true
irb(main):002:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_decimal(1000) => "1.00 kilobyte"
irb(main):003:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_decimal(10000) => "10.00 kilobytes"
irb(main):004:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_decimal(100000) => "100.00 kilobytes"
irb(main):005:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_decimal(10 ** 13) => "10.00 terabytes"
To convert bytes to binary suffixes:
irb(main):006:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_binary(1000) => "1000.00 bytes"
irb(main):007:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_binary(10000) => "9.77 kibibytes"
irb(main):008:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_binary(100000) => "97.66 kibibytes"
irb(main):009:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_binary(10 ** 13) => "9.09 tebibytes"
To convert them to short Metric decimal suffixes:
irb(main):010:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_decimal(1000) => "1.00 kB"
irb(main):011:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_decimal(10000) => "10.00 kB"
irb(main):012:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_decimal(100000) => "100.00 kB"
irb(main):013:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_decimal(10 ** 13) => "10.00 TB"
To convert them to short IEC binary suffixes:
irb(main):014:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_binary(1000) => "1000 B"
irb(main):015:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_binary(10000) => "9.77 KiB"
irb(main):016:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_binary(100000) => "97.66 KiB"
irb(main):017:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_binary(10 ** 13) => "9.09 TiB"
It can support values upto hundreds of yottabytes and yobibytes, or yb and yib. You can also do stuff like:
$ irb irb(main):001:0> require 'linux_stat' => true
irb(main):002:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_decimal(LinuxStat::Mounts.device_stat('/dev/sdb1')[:total]) => "31.47 GB"
irb(main):003:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_binary(LinuxStat::Mounts.device_stat('/dev/sdb1')[:total]) => "29.31 GiB"
irb(main):004:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_binary(LinuxStat::Mounts.device_stat('/dev/sdb1')[:used]) => "26.80 GiB"
irb(main):005:0> LinuxStat::PrettifyBytes.convert_short_binary(LinuxStat::Mounts.device_stat('/dev/sdb1')[:available]) => "2.51 GiB"
Read the ri documentation for more info.
---
## Return Types
+ In general, if a method returns either a Float or a Integer or a Time, it will return a Float or Integer or Time in all cases. But if the status isn't available, it will return nil.
+ If the method returns a Hash / Array, it will return return Hash / Array in all cases. If the status isn't available, it will return an empty Hash / Array.
+ If the method returns a String, it will return return String in all cases. If the status isn't available, it will return an empty *frozen* String.
+ It doesn't have implementation of any Error that gets raised in runtime for the ease of use.
+ If you need to check some stat that returns an integer or float, and you get nil, you know it's not available, so you can work accordingly. But if you need the integer or float value in 0 to whatever format, you can use the .to_i or .to_f method on the object, nil will get converted to number then.
If some error is *raised* it should be reported as a bug.
---
## Ruby on Rails
1. Just add `gem linux_stat`:
$ bundle add linux_stat
You can use LinuxStat directly in rails.
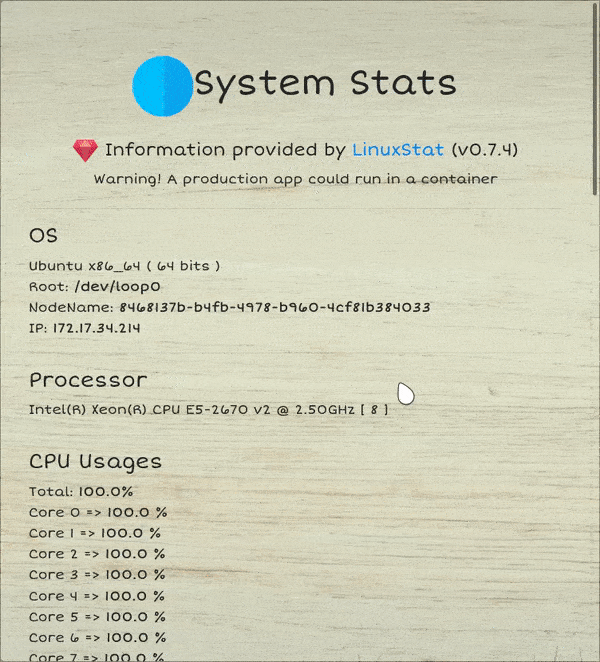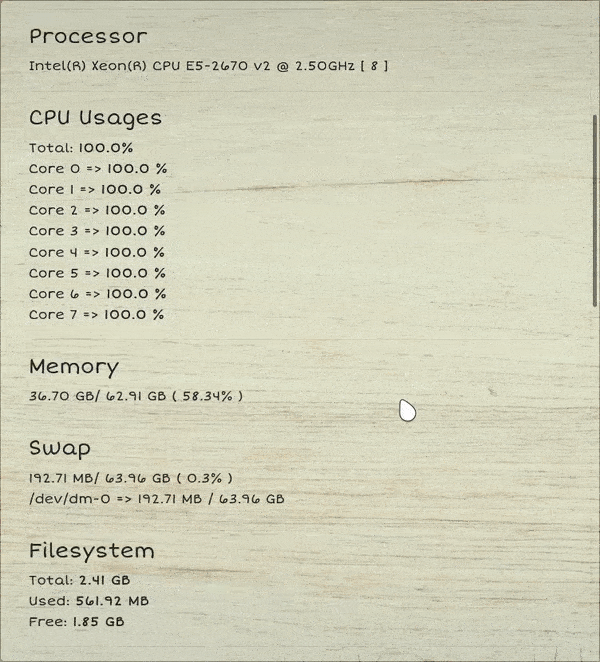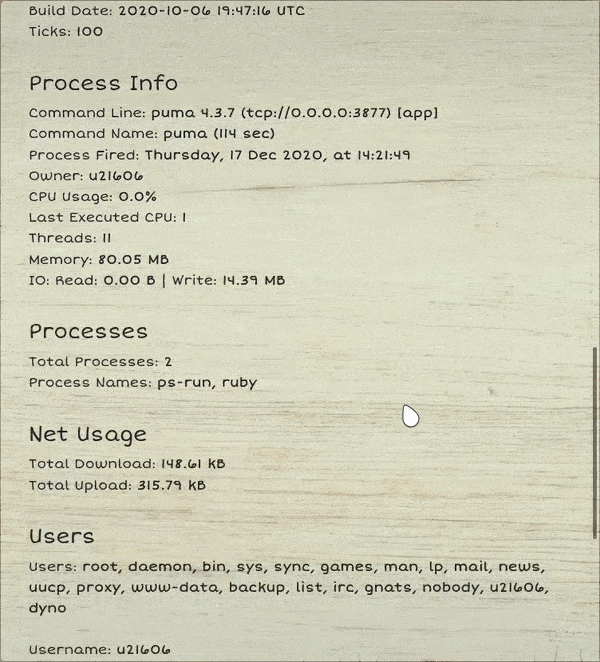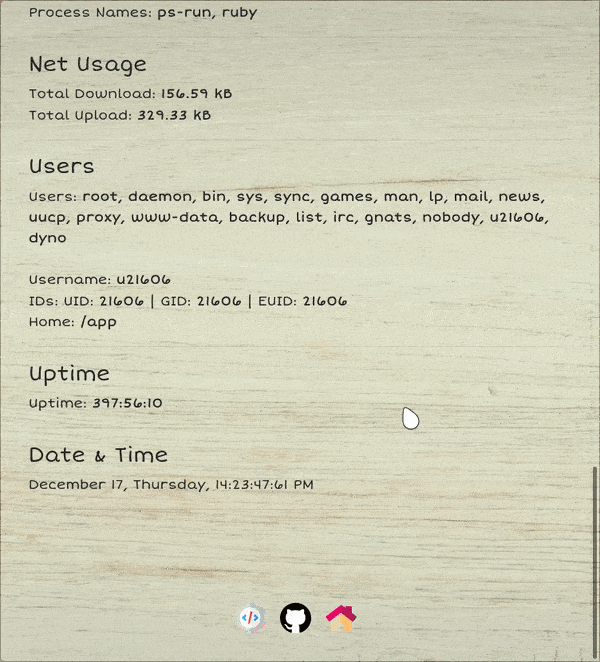
---
## Android
LinuxStat does support Android OS. But it's not rigorously tested on all device like android apps.
But in Termux you can just run LinuxStat without facing issues.
Note that the CPU count can differ due to hotplugging feature. So if you see the CPU count changes, there's not really nothing to do about that.
Issues regarding running LinuxStat on termux are also welcomed.
---
## Development
After checking out the repo, compile and install this gem onto your local machine with `bundle exec rake install`
You can also run `bin/console` for an interactive prompt that will allow you to experiment.
To test all modules, run `rake install` and then `exe/linuxstat.rb`. Also check "Testing" below.
---
## Testing
Like other gems, this doesn't have a test like RSpec.
We suggest using the exe/linuxstat.rb file on various Linux systems to test.
First you need to execute `bundle exec rake install` to compile and install this gem.
If you need to test a specific module, say the CPU, just run it like this:
$ ruby exe/linuxstat.rb CPU
Or:
$ ruby exe/linuxstat.rb cpu
That is, the argument passed is not case-sensitive.
But if the argument passed isn't available and outright wrong, it will run all the module methods. For example, you can't do:
$ ruby exe/linuxstat.rb upc
This is not a valid module and can't be run.
---
## Contributing
Bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub at https://github.com/Souravgoswami/linux_stat.
---
## License
The gem is available as open source under the terms of the [MIT License](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT).